Web Service #
The Web Service is deprecated, use Aggregator CLI instead.
Visual Studio Team Services (VSTS) and TFS (2015 and later) can integrate with other systems through Service hooks. TFS Aggregator Web Service leverage the Web Hooks variant to receive notifications of work items changes in VSTS/TFS.
The common scenario is:
- A user changes some work item’s data using Visual Studio or TFS Web Interface, then presses the Save button (or hits
Ctrl-S); - VSTS/TFS validates the edit and saves the changes to the database;
- VSTS/TFS call the Aggregator Web Service using HTTPS, the message contains information on the type of change, the instance, project and work item;
- Aggregator see which Rules apply and execute them, which may call back the loading additional work items;
- Aggregator calls back VSTS/TFS using HTTPS to save any changed work item.
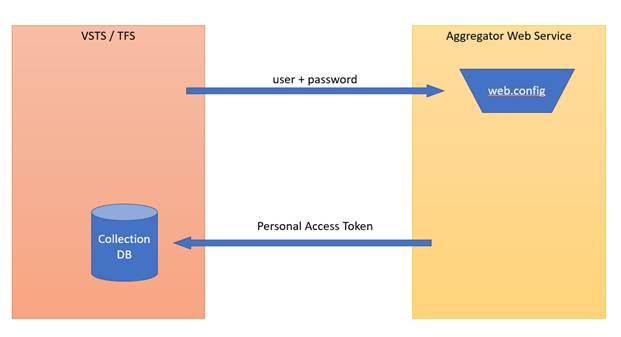
Note that steps 3 and 5 requires authentication.
Server Plugin #
The following diagram may help understand the control flow.
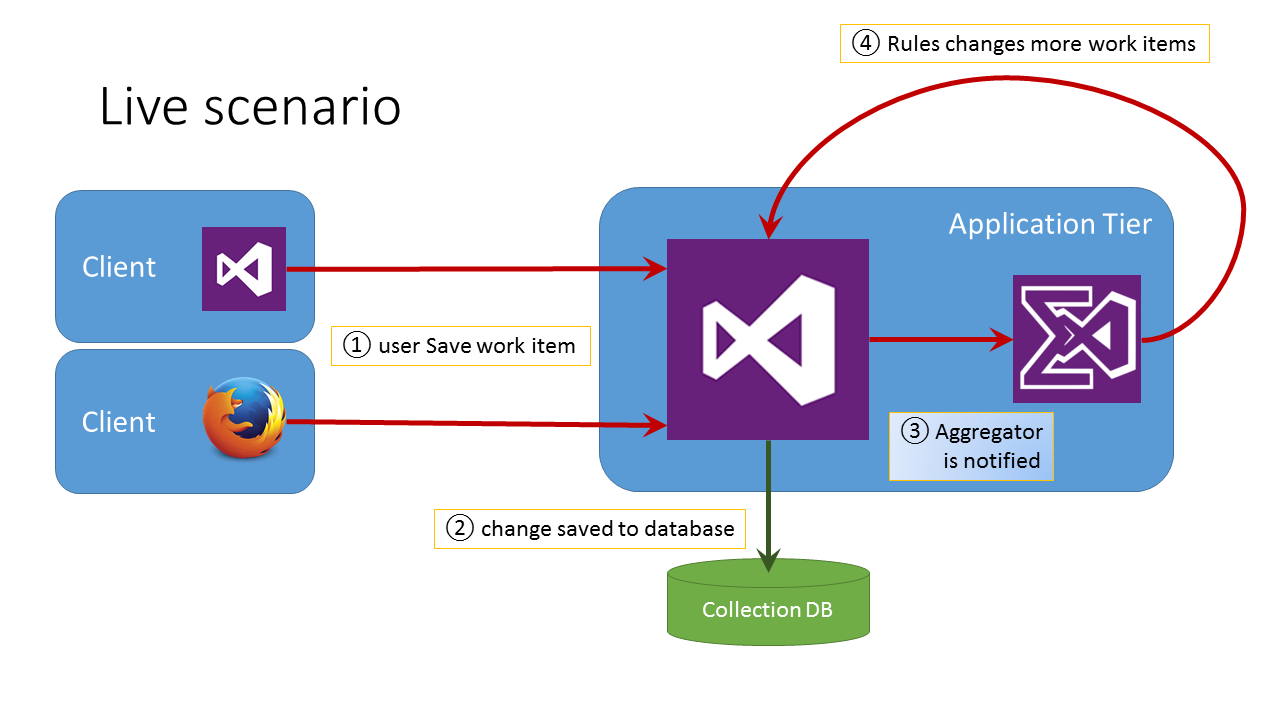
- A user changes some work item’s data using Visual Studio or TFS Web Interface, then presses the Save button (or hits
Ctrl-S); - TFS validates the edit and saves the changes to the database;
- TFS notifies the Aggregator plugin of the ID of the changed work item
- Aggregator see which Rules apply and execute them, which may cause the loading and saving of additional work items.
Note that step 4 may trigger Aggregator again on the just saved work items.
Keep also in mind that scripts and applications can change work items without user intervention, like Team Foundation Server Integration Tools. Make sure that TFS Aggregator kicks in only when intended.
Configuration changes #
Aggregator loads and parses the Rules from TFSAggregator2.ServerPlugin.policies file at first run. The result is cached in memory and the cache invalidates if the file changes.